Guarino Guarini Paintings
Guarino Guarini was an Italian architect, priest, mathematician, and theologian, born on January 17, 1624, in Modena, Italy. He was a member of the Theatine order, which he joined in 1639, dedicating his life to both religious and intellectual pursuits. Guarini received his education in Rome, studying theology, philosophy, and mathematics. His intellectual curiosity and diverse interests would greatly influence his architectural style, which combined structural complexity with a profound sense of spirituality.
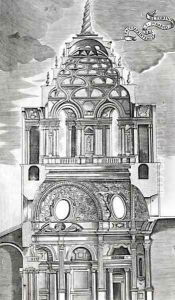
Guarini's architectural career took off when he was in his thirties, after he took up residence in Turin in 1666 under the patronage of Duke Carlo Emanuele II of Savoy. He became the court architect and engineer, and it was during this time that he produced his most notable work, the Chapel of the Holy Shroud (Cappella della Santa Sindone) in Turin, completed in 1694. This chapel is attached to the Turin Cathedral and was designed to house the Shroud of Turin, a relic believed by many to be the burial cloth of Jesus Christ. Guarini's design for the chapel is renowned for its use of light, geometric complexity, and the interplay of structure and space - characteristics that exemplify the Baroque style of architecture.
Apart from his architectural contributions, Guarini also published several books on mathematics and philosophy. His architectural treatise, 'Architettura Civile,' was published posthumously in 1737 and demonstrates his extensive knowledge of geometry and his innovative approach to design, which often involved complex spatial arrangements and the use of light as a structural element.
Guarini left a significant legacy in the Piedmont region of Italy and beyond, with works that include the Palazzo Carignano and the Church of San Lorenzo in Turin. His influence can be seen in the works of later architects and in the development of Baroque and Rococo architecture. Guarini died on March 6, 1683, in Milan, leaving behind a body of work that continues to be studied and admired for its inventive and dynamic approach to design and construction.