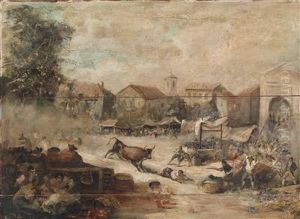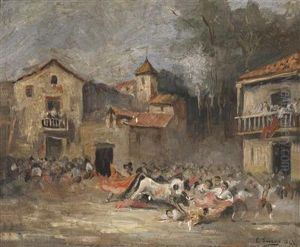Eugenio Lucas Velasquez Paintings
Eugenio Lucas Velázquez was a Spanish painter known for his work within the Romantic movement, particularly noted for his paintings that reflect the influence of Francisco Goya, whose works he admired. Born in Madrid on February 9, 1817, Lucas Velázquez showed an inclination towards the arts at a young age.
His early education is not well-documented, but it is known that he didn't receive a formal academic training from the Royal Academy of Fine Arts of San Fernando in Madrid, unlike many artists of his time. Instead, he developed his skills independently and was greatly influenced by the work of Goya, whose paintings he had the opportunity to study firsthand as many were housed in Madrid.
Throughout his career, Eugenio Lucas Velázquez produced a wide range of works, including genre scenes, landscapes, and historical paintings. He is particularly remembered for his bullfighting scenes, a subject that was also famously captured by Goya. His work was characterized by a dynamic use of brushwork and a vivid portrayal of the Spanish life and culture.
Lucas Velázquez's style evolved over time, initially reflecting the dark tones and dramatic lighting of Goya's influence, but later incorporating a brighter palette and looser brushstrokes as he developed his own artistic voice. Despite his lack of formal training, his skill earned him recognition and he was commissioned to create works for various clients, including members of the Spanish nobility.
In addition to painting, Eugenio Lucas Velázquez also worked in other mediums such as drawing and printmaking. He created a series of lithographs that were well received and demonstrated his versatility as an artist.
Lucas Velázquez's work was appreciated during his lifetime, and he enjoyed a degree of success. He exhibited his works in various exhibitions, including the National Exhibition of Fine Arts in Spain, where he received awards for his paintings.
Eugenio Lucas Velázquez died on September 11, 1870, in Madrid. His legacy is preserved in the collections of several museums, including the Prado Museum in Madrid, where some of his most important works are displayed. His contribution to Spanish Romanticism remains significant, and his works continue to be studied and admired for their unique blend of Goya's influence and Lucas Velázquez's distinctive style.